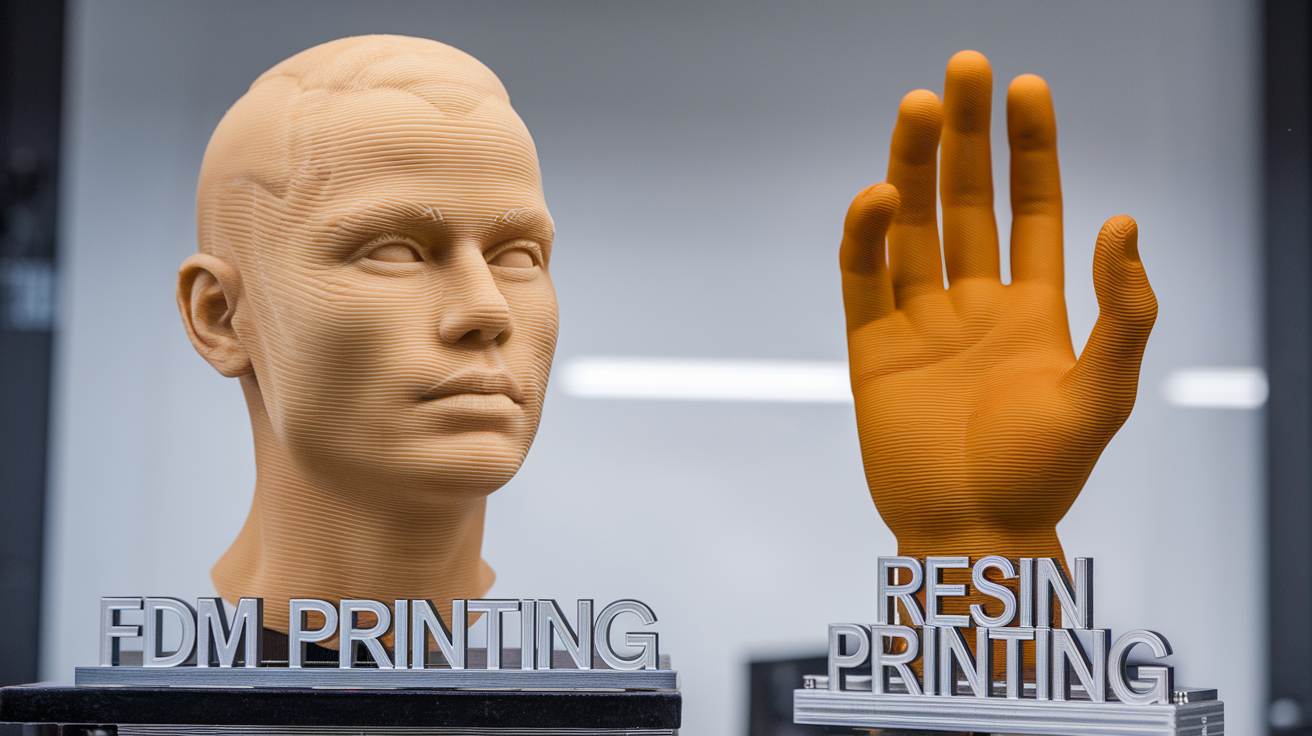
Introduction to 3D Printing Technologies
Three-dimensional (3D) printing has revolutionized manufacturing, prototyping, and even hobbyist projects. Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) and Resin printing are two of the most popular technologies. Understanding the differences between them can help you choose the best printer for your needs.
Understanding FDM Printers
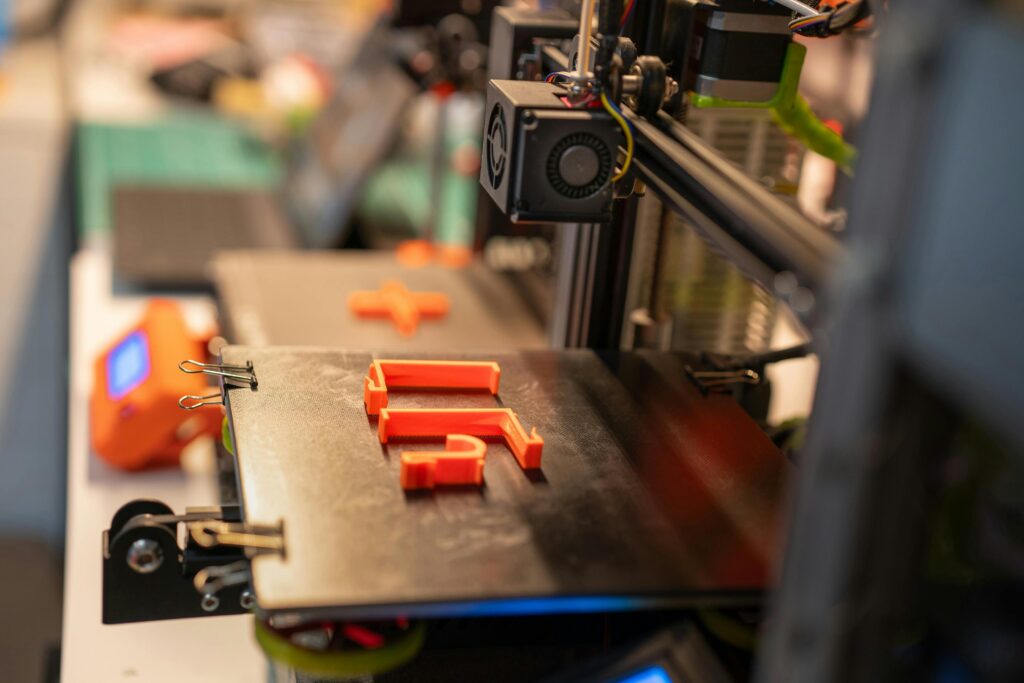

FDM printers work by extruding thermoplastic filaments through a heated nozzle, which then solidify layer by layer to build the final object. These printers are known for their ease of use and affordability, making them a popular choice for beginners and professionals alike. They generally produce durable objects but might struggle with fine details and smooth surface finishes.
Advantages of Resin Printers
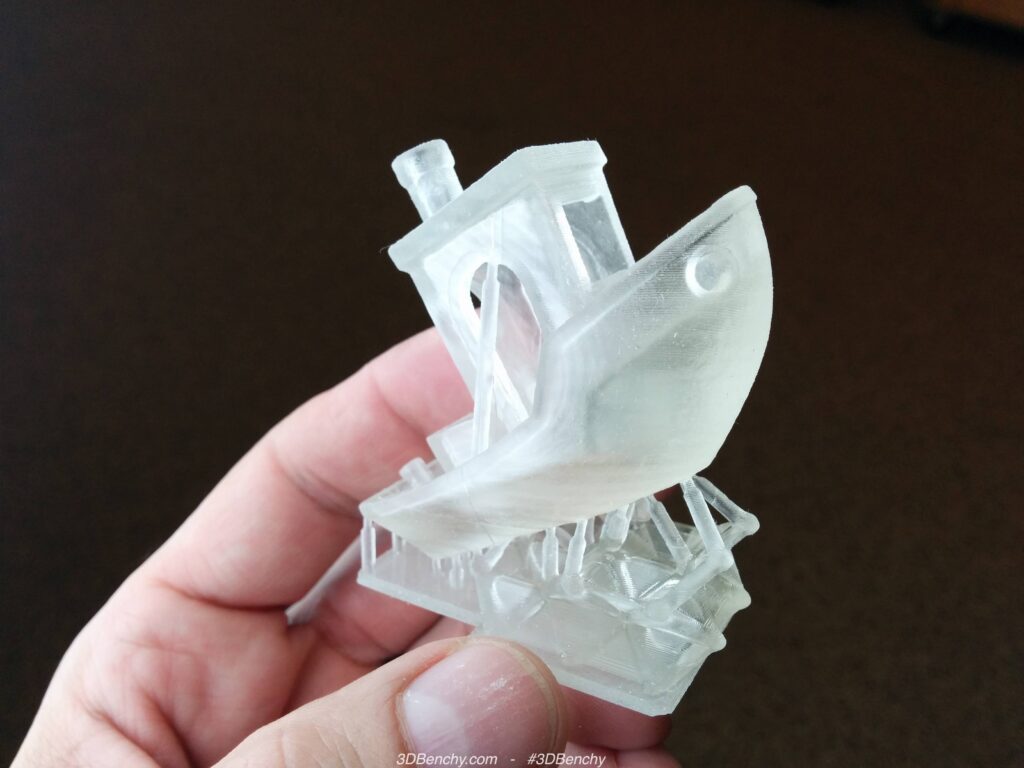

Resin printers, on the other hand, use a light source (like UV light) to cure liquid resin layer by layer in a process called photopolymerization. This technology is known for producing highly detailed models with fine surface finishes. However, resin printers tend to be more expensive and require more maintenance, including careful handling and disposal of resin materials.
Best Printers for Different Needs
When choosing between FDM and resin printers, consider your specific requirements. If you need strong, functional parts on a budget, an FDM printer is likely your best bet. For detailed miniatures, jewelry, or prototypes needing high precision, a resin printer will be more suitable despite the higher costs and upkeep.
Conclusion
Both FDM and resin printers have their unique advantages and drawbacks. FDM is often the go-to for functional, durable parts and affordability, while resin printers excel in detailed, high-quality prints. By understanding what each technology offers, you can make an informed decision on which 3D printer best fits your projects.