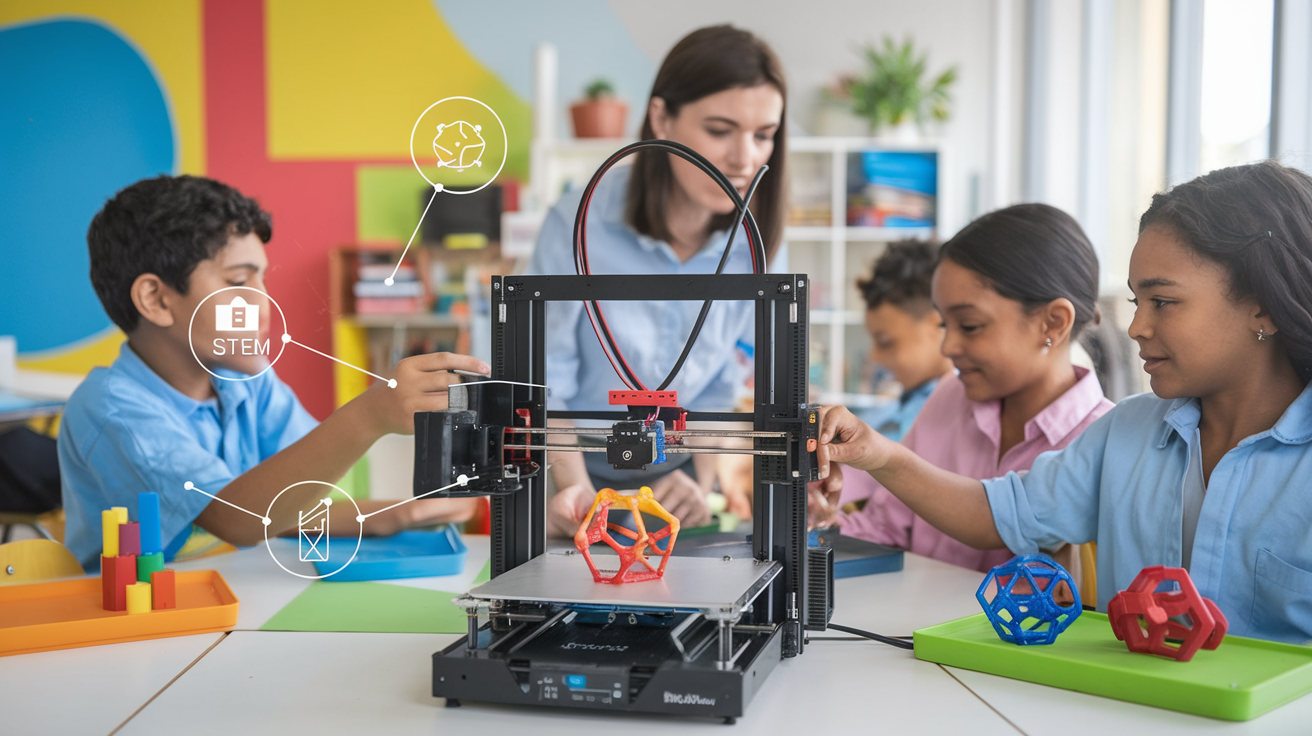
Introduction to 3D Printing in Education
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process where three-dimensional objects are created by layering material based on digital models. Initially developed in the 1980s, 3D printing technology has evolved dramatically, transforming from rudimentary machines to sophisticated systems capable of producing complex structures with a variety of materials. This evolution has broadened the potential applications of 3D printing across various industries, including healthcare, manufacturing, and now, education.
In recent years, the integration of 3D printing into educational settings has witnessed a significant rise globally. Schools and educational institutions are recognizing the value of this transformative technology in enhancing the learning experience. By providing a hands-on, interactive approach to education, 3D printers enable students to bring their ideas to life, fostering creativity and innovation. The incorporation of 3D printing in classrooms is not limited to any single subject; it spans across disciplines such as science, technology, engineering, arts, and mathematics (STEAM).
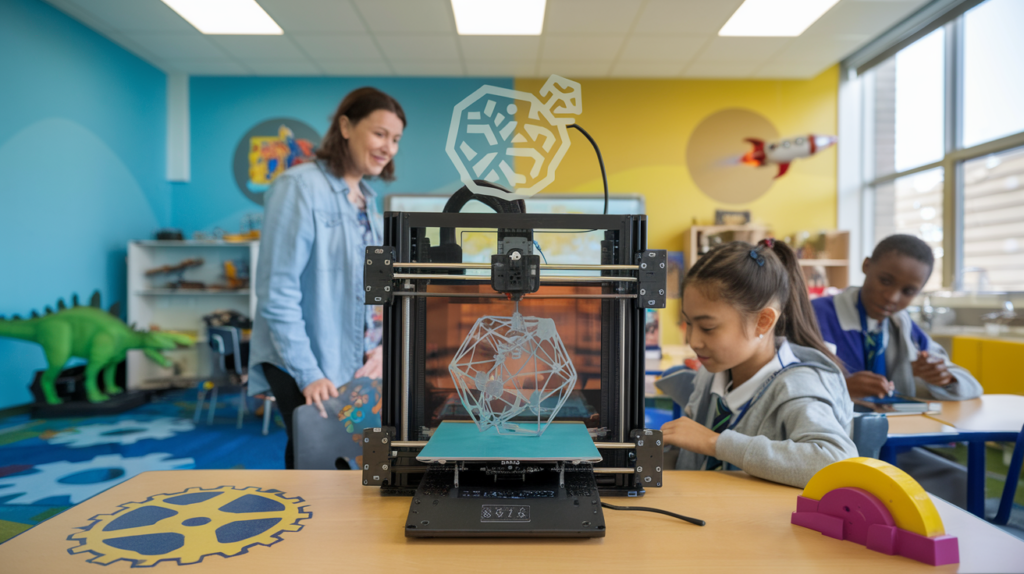

The importance of introducing 3D printing in education lies in its potential to revolutionize traditional teaching methods. Unlike conventional lecture-based instruction, 3D printing offers a practical, engaging, and experiential form of learning. Students can design and fabricate tangible models, aiding in the comprehension of abstract concepts and promoting problem-solving skills. For instance, in a biology class, learners can print anatomical models to better understand human anatomy, while in mathematics, geometric shapes can be printed to visualize complex theorems.
Moreover, 3D printing allows for individualized learning experiences, accommodating different learning styles and paces. Educators can tailor projects that cater to the unique interests and strengths of their students, making the learning process more personalized and effective. As the technology continues to advance, the accessibility of 3D printers is increasing, making it feasible for more schools to integrate this cutting-edge tool into their curriculum.

Globally, educational institutions are embracing 3D printing, recognizing its potential to enhance practical learning and prepare students for future technological advancements. By exposing students to this technology, schools are not only enriching the educational experience but also equipping the younger generation with the skills and knowledge necessary to thrive in an increasingly technologically driven world.
Educational Benefits of 3D Printing
3D printing has significantly reshaped the educational landscape by offering direct and indirect benefits that enhance students’ learning experiences. One of the most profound impacts of 3D printing in education is in the realm of STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) subjects. By integrating 3D printing technology into the curriculum, students are afforded a hands-on approach to learning complex concepts. For instance, in biology, students can print 3D models of organs or cells, which allows them to observe and understand biological structures in a tangible way that textbooks cannot offer. This method of learning not only heightens engagement but also sparks a deeper interest in STEM fields.

Beyond enhancing engagement in STEM subjects, 3D printing ignites creativity and fosters innovation among students. The ability to materialize their ideas and designs promotes a sense of achievement and encourages students to think outside the box. For example, art and design classes can leverage 3D printers to bring students’ digital drawings to life, allowing for a more immersive and interactive art education. This process helps develop students’ creative problem-solving skills, as they must overcome the challenges of translating a 2D sketch into a 3D model.
Moreover, 3D printing cultivates critical problem-solving abilities. The process of designing and printing objects requires students to understand and manage various software, materials, and the mechanical intricacies of 3D printers. Students often encounter obstacles that require them to troubleshoot and find effective solutions, thereby honing their analytical and critical thinking skills. An exemplary case of this is seen in engineering classes where students design and prototype mechanical parts, iteratively refining their designs based on trial and error. This experiential learning process is invaluable in preparing students for real-world engineering challenges.
Overall, the integration of 3D printing in education has led to remarkable improvements in student engagement, nurturing of creativity and innovation, and the development of essential problem-solving skills. These benefits, coupled with the tangible examples of successful implementation, underscore the transformative potential of 3D printers in modern education.
Practical Applications in the Classroom
3D printing has become a transformative tool in educational settings, providing students with hands-on learning opportunities and enhancing traditional teaching methods. Across various subjects and grade levels, educators are incorporating 3D printing technology to foster deeper understanding and engagement among students.
In history lessons, 3D printers are used to create replicas of historic artifacts, giving students a tangible connection to the past. For instance, a high school in California printed ancient Greek vases, allowing students to examine the intricacies of ancient pottery up close, significantly enriching their understanding of historical craftsmanship.

Biology classes also benefit from 3D printing, with educators using the technology to produce biological models. These models range from simple cell structures to complex human organs, providing a clear, three-dimensional view that is not possible with traditional textbooks. A notable example is a middle school in New York, where students printed detailed models of the human heart. This allowed them to visualize and comprehend the anatomy and function of the organ more effectively.
In engineering and technology courses, students are given the opportunity to design and prototype their projects using 3D printers. This practical approach not only enhances their technical skills but also encourages creativity and problem-solving. For example, a high school robotics club in Texas utilized 3D printing to create custom parts for their competition robots, leading to innovative designs and improved performance in contests.
Art classes are not left behind either; 3D printing opens up new avenues for creative expression. Students can design and print intricate sculptures or even functional items like vases and jewelry. A notable case is an art school in Florida where students designed and printed custom masks for a school play, merging technology with theatrical arts to produce a visually stunning performance.
Case studies from schools globally show the successful integration of 3D printing into the curriculum, highlighting its significant impact on student engagement and learning outcomes. As these examples demonstrate, 3D printing is not just a supplementary tool but a pivotal element that enriches the educational experience across diverse subjects.
Challenges and Future Prospects of 3D Printing in Education
Integrating 3D printing technology into educational institutions presents a series of unique challenges. One of the primary hurdles is the cost. 3D printers, while increasingly affordable, still represent a significant investment for many schools, especially those operating with limited budgets. The cost extends beyond the hardware to include ongoing expenses related to materials, maintenance, and software updates.
Another significant challenge is the requirement for specialized teacher training. Educators must be proficient not only in operating the 3D printers but also in effectively integrating them into their curriculum. Professional development programs specifically tailored to 3D printing can be both time-consuming and financially burdensome for schools.

Curriculum development itself poses another layer of complexity. It requires careful planning to ensure that 3D printing activities are aligned with educational standards and learning objectives. Schools need to develop resources and lesson plans that maximize the potential of this technology in enhancing student learning experiences.
Despite these challenges, the future prospects of 3D printing in education are promising. To tackle cost-related issues, several solutions are emerging. Schools can seek grants, sponsorships, or crowd-funding efforts to raise the necessary funds. Additionally, companies specializing in 3D printing frequently offer educational discounts and starter packages designed to be budget-friendly.
For teacher training, a variety of online courses and workshops are available, enabling instructors to gain the necessary skills at their own pace. Collaborations with universities and tech companies can also provide valuable support and resources. Industry partnerships might facilitate access to the latest technology and innovations.
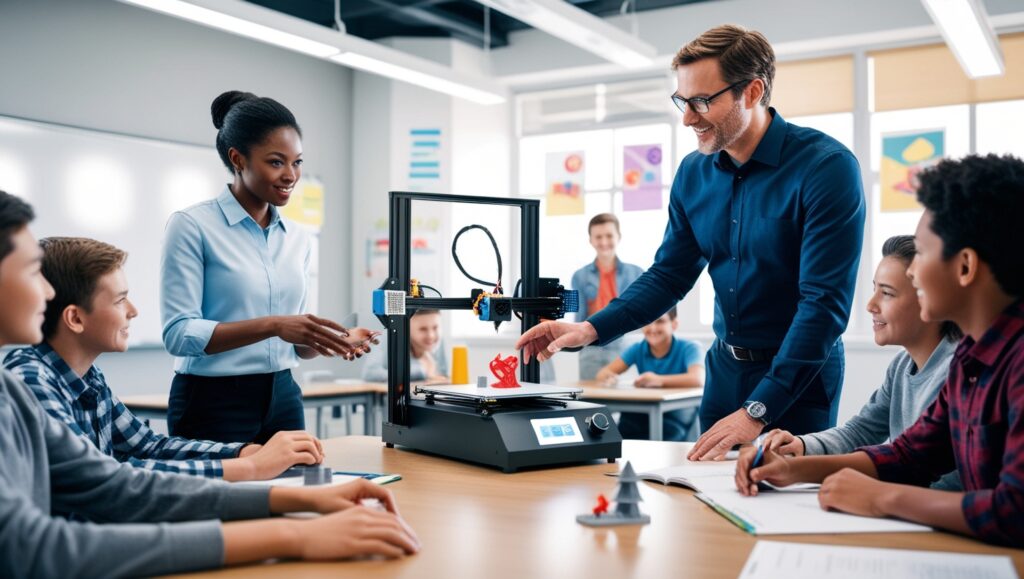

The evolution and impact of 3D printing in education look set to continue upward. Advances in 3D printing technology are likely to further lower costs and improve accessibility, making it feasible for a wider range of schools to participate. Enhanced software and user-friendly interfaces will make it easier for teachers and students to utilize this technology effectively. As 3D printing becomes more ingrained in educational paradigms, it has the potential to revolutionize the way we approach problem-solving, creativity, and hands-on learning in classrooms globally.





