Introduction to 3D Printing Software
3D printing software is pivotal in transforming digital designs into tangible objects, serving as the backbone of the 3D printing workflow. These software solutions encompass several critical functions that streamline the creation process, making them indispensable tools for hobbyists, professionals, and industries alike. The primary functions of 3D printing software fall into three broad categories: 3D modeling, slicing, and printer control.
3D modeling is the initial step where users design the three-dimensional objects they wish to print. This process requires computer-aided design (CAD) tools that offer intricate detailing and flexibility. Engineers, designers, and artists utilize these tools to create complex geometries and prototypes, pushing the boundaries of what can be materialized.
After the 3D model is complete, the next crucial phase is slicing. Slicing software takes the 3D model and divides it into horizontal layers, generating the instructions required for the 3D printer to construct the object layer-by-layer. This step is vital for ensuring the object’s structural integrity and overall quality. The precision in slicing directly impacts the final output, making this a critical aspect of the entire operation.

The third function is printer control, which involves the actual management of the 3D printer during the printing process. This includes managing temperature settings, speed, and material flow, ensuring that the printer operates smoothly and efficiently. Advanced printer control software also offers real-time monitoring and adjustments, providing users with the capability to correct issues on-the-fly.
The growing popularity of 3D printing spans multiple industries, making these software tools even more significant. In manufacturing, 3D printing streamlines prototyping and production lines, offering unprecedented customization and speed. The healthcare industry leverages 3D printing for creating medical devices, prosthetics, and even bio-printed tissues. Education benefits by incorporating 3D printing to foster innovation and hands-on learning experiences for students. As 3D printing continues to proliferate, the importance of reliable and efficient 3D printing software cannot be overstated.
Free 3D Printing Software Options
When diving into the world of 3D printing, finding the right software is crucial. Fortunately, several free 3D printing software options are available, each with unique features and capabilities. This section explores a few of the most popular tools, namely Tinkercad, Ultimaker Cura, and Blender.

- Tinkercad is an excellent entry point for beginners. Developed by Autodesk, Tinkercad is known for its user-friendly interface and ease of use. The software allows users to create 3D models with simple drag-and-drop features, making it accessible to those with little to no prior experience in 3D design. While Tinkercad’s simplicity is a significant advantage, it may not offer the advanced features that experienced designers might seek. However, its broad compatibility with various 3D printers makes it a top choice for educational purposes and hobbyists.
- Ultimaker Cura is another highly-regarded free software within the 3D printing community. This open-source slicing program excels in its ability to convert 3D models into printable files. Ultimaker Cura is highly customizable, allowing users to fine-tune settings for optimal print results. It supports a wide array of 3D printers, including models not produced by Ultimaker. Despite its robust features, beginners might find the extensive array of settings overwhelming. Nevertheless, once mastered, it proves to be an invaluable tool for achieving high print quality.
- Blender offers extensive 3D modeling capabilities and is entirely free to use. This software is ideal for users who require advanced modeling functions that go beyond basic 3D printing needs. Blender’s complexity allows for intricate designs and detailed sculptures, positioning it well beyond a simple slicer or beginner’s tool. However, its steep learning curve can be a challenge for those new to 3D modeling. While Blender is a powerful free option, integrating it with 3D printing workflows may necessitate supplementary software for slicing and printer compatibility.
Despite their limitations compared to paid options, these free 3D printing software tools provide a strong foundation for anyone interested in 3D printing. From user-friendly interfaces for newcomers to highly customizable and advanced features for seasoned users, there is a free solution suited to a variety of needs and skill levels.
Paid 3D Printing Software Options
When evaluating the extensive array of 3D printing software, it becomes clear that paid options often furnish a suite of advanced features and specialized tools that exceed the capabilities of their free counterparts. Many professional and hobbyist users find the additional investment worthwhile for the enhanced functionalities and superior outcomes in their 3D printing projects.

One prominent player in this domain is Fusion 360 by Autodesk. Known for its comprehensive suite of professional-grade 3D modeling tools, Fusion 360 facilitates intricate design work with parametric, direct, and surface modeling capabilities. Its cloud-based collaboration features also enable multiple team members to work together seamlessly. The pricing model for Fusion 360 is subscription-based, with options starting from $60 per month, making it accessible for both individual creators and larger organizations.

Simplify3D is another essential paid software for 3D printing enthusiasts, renowned for its advanced slicing features that significantly improve the quality of printed objects. Simplify3D excels in offering customizable support structures, variable layer heights, and pre-configured profiles for thousands of 3D printers. These enhancements help users achieve more precise and detailed prints. Simplify3D operates on a one-time purchase model, priced at approximately $149, which provides lifetime access to the software without recurring subscription fees.
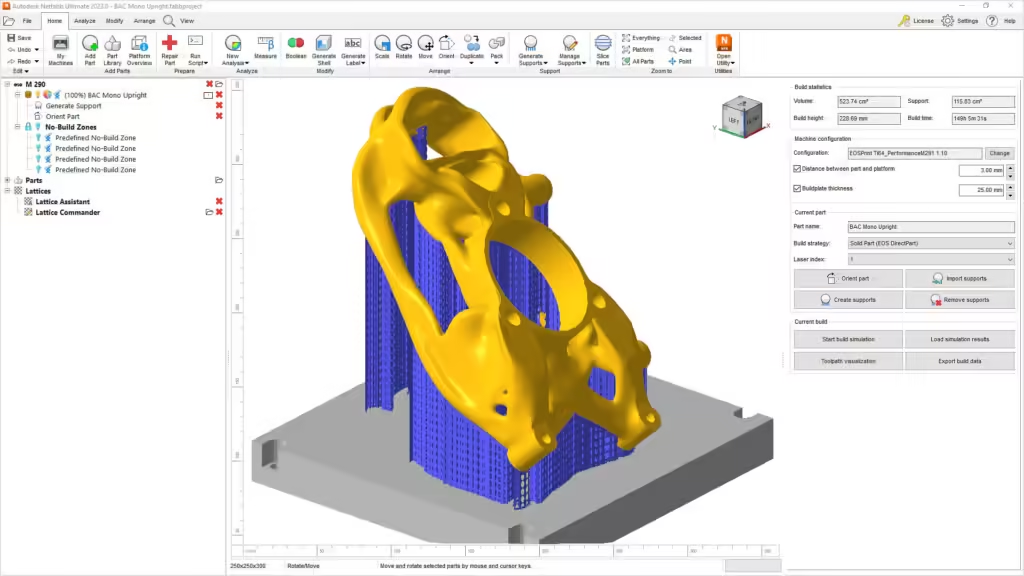
Additionally, Autodesk Netfabb specializes in preparing complex models for 3D printing, focusing on optimizing models and minimizing errors. The software includes tools for error detection, repairing meshes, and generating supports optimized for various printing methods. Netfabb’s suite of tools also includes advanced packing algorithms, making it ideal for manufacturing environments. Netfabb offers a tiered subscription pricing model, starting at around $200 per year, which caters to different levels of usage and professional needs.
In conclusion, paid 3D printing software such as Fusion 360, Simplify3D, and Autodesk Netfabb empower users with robust functionalities that streamline complex 3D printing projects. These tools not only enhance the overall quality and precision of prints but also provide a professional-grade experience that can significantly elevate the capabilities of 3D printing enthusiasts and professionals alike.
Comparison and Recommendations
Selecting the right 3D printing software can be a daunting task, given the plethora of options available on the market. To ease this decision-making process, we have compiled a detailed comparative analysis of both free and paid options, highlighting features, pricing, usability, and more. The table below illustrates the key attributes, making it easy to determine the best fit based on your specific needs.
| Software | Price | Features | Usability | User Experience | Community Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Software A (Free) | Free | Basic modeling tools, limited file formats | Easy for beginners | Intuitive UI | Large, active community |
| Software B (Paid) | $50/month | Advanced modeling, extensive file formats | Steep learning curve | Professional-grade UI | Dedicated support team |
When evaluating the available 3D printing software, consider your current skill level and the complexity of your projects. For beginners, Software A offers an easy introduction to 3D modeling with a user-friendly interface and strong community support, which is crucial for troubleshooting and learning. The free cost is also an appealing factor for users new to 3D printing who may not want to invest heavily upfront.
On the other hand, professional users or those working on more complex projects may find Software B more suitable despite its cost. Its advanced features and professional-grade user interface make it ideal for commercial or intricate designs. However, note the steeper learning curve, which might require additional time investment.
Hobbyists or intermediate users would benefit from a balanced approach, selecting software that offers a mix of advanced features without an overly complex interface. Paid options like Software C may provide such a balanced experience with moderate pricing and good community support.
In summary, the best 3D printing software depends on individual needs and expertise levels. Whether you are a beginner, hobbyist, or professional, there are suitable tools available that cater to all levels. Choose wisely based on the comparative insights provided to optimize your 3D printing endeavors.