Introduction to Common 3D Printing Issues
3D printing technology has transformed various sectors, ushering in a new era of manufacturing and creative possibilities. However, it is not devoid of challenges. As with any advanced technology, users often encounter a range of issues that can disrupt the 3D printing process. These issues span from material inconsistencies and design flaws to hardware malfunctions, each posing unique obstacles to achieving optimal results.
Understanding these common issues is crucial for both novice and experienced users. By familiarizing oneself with typical 3D printing problems, such as layer shifting, warping, and weak infill, one can better prepare for troubleshooting and resolution. This proactive approach not only conserves valuable resources like time and materials but also enhances the overall effectiveness of the 3D printing experience.

Effective troubleshooting begins with early recognition of potential problems. For instance, spotting filament feed issues or adhesion problems during the initial stages can prevent complete print failures, which are often more costly and time-consuming to rectify. By addressing these issues promptly, users can maintain the integrity and quality of their prints.
Moreover, understanding the underlying causes of these problems enables better decision-making when it comes to settings adjustments, material choices, or even hardware upgrades. For example, knowing that certain filaments are more prone to warping can lead to informed decisions about print bed temperature or the use of specific adhesives to improve bed adhesion.
In summary, having a comprehensive knowledge of the common 3D printing issues and their solutions is essential for anyone involved in 3D printing. It equips users with the skills to navigate the intricacies of the technology effectively, ensuring a smoother, more efficient printing process that maximizes the potential of their 3D printer. As we delve deeper into this blog post, we will explore these common problems in detail and provide practical solutions to help you overcome them.
Poor Bed Adhesion
Poor bed adhesion is a common issue that can compromise the quality of your 3D prints. Signs include the print not sticking to the bed, warping, or the first layer not forming properly. Potential causes include an unlevel bed, incorrect bed temperature, or dirty bed surfaces. To fix this, start by leveling the bed carefully. Use a piece of paper to check the distance between the nozzle and the bed at different points. Adjust as necessary. Clean the bed surface with isopropyl alcohol to remove any oils or dust that might hinder adhesion. Additionally, make sure you are using the correct bed temperature and material-specific adhesives, such as painter’s tape or glue stick.

Extruder Issues
Extruder issues appear when the printer fails to feed filament properly, resulting in under-extrusion or even stopping altogether. Common signs of extruder problems include clicking noises, uneven filament extrusion, and gaps in print layers. These issues can be caused by tension imbalances, clogged gears, or worn-out components. To resolve this, start by ensuring the filament path is clear and clean. Adjust the tension screws to ensure the filament is adequately gripped but not overly compressed. Regularly maintain and, if needed, replace parts like the PTFE tube or extrusion gear.
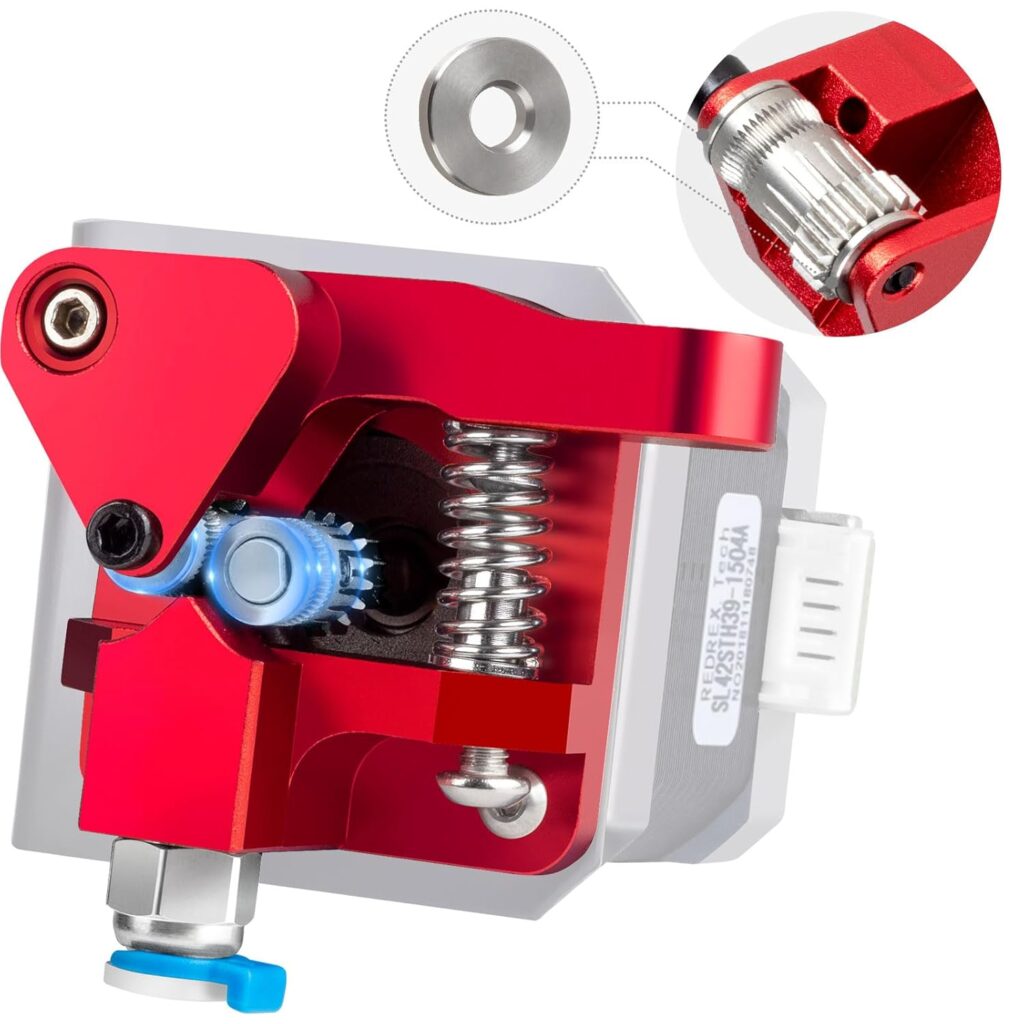

Filament Tangles and Breaks
Tangled or breaking filament can disrupt prints, leading to incomplete models or printer malfunctions. Indicators of this problem are visible filament knots or breaks mid-print. Causes typically include poor storage practices, inconsistent filament diameter, or printer settings. Prevent tangles by properly storing filament spools in a dry, dust-free environment, ensuring they are wound evenly. Check the filament diameter for consistency before use. Adjust print speed and temperature settings to accommodate the specific filament being used.

Layer Shifting
Layer shifting is characterized by layers misaligning, leading to prints with slanted sections or horizontal steps. Causes often involve mechanical issues such as loose belts, misaligned axes, or obstructions in the printer path. Begin troubleshooting by checking and tightening belts and pulleys, ensuring they have the right tension. Inspect the axes for any physical obstructions or debris. Regularly calibrate the printer’s stepper motors and monitor the printer during operation to catch and resolve any issues promptly.
Clogged Nozzles
A clogged nozzle can halt printing entirely or cause inconsistent filament flow, resulting in poor-quality prints. Signs of this problem include no filament extrusion or irregular output. Causes often include filament debris, overheating, or incorrect retraction settings. To fix a clogged nozzle, start by heating it to the appropriate temperature and manually extruding filament to dislodge any debris. If the clog persists, use a thin tool or specialized cleaning filament to clear the obstruction. Ensure regular nozzle maintenance and fine-tune retraction settings to prevent future clogs.
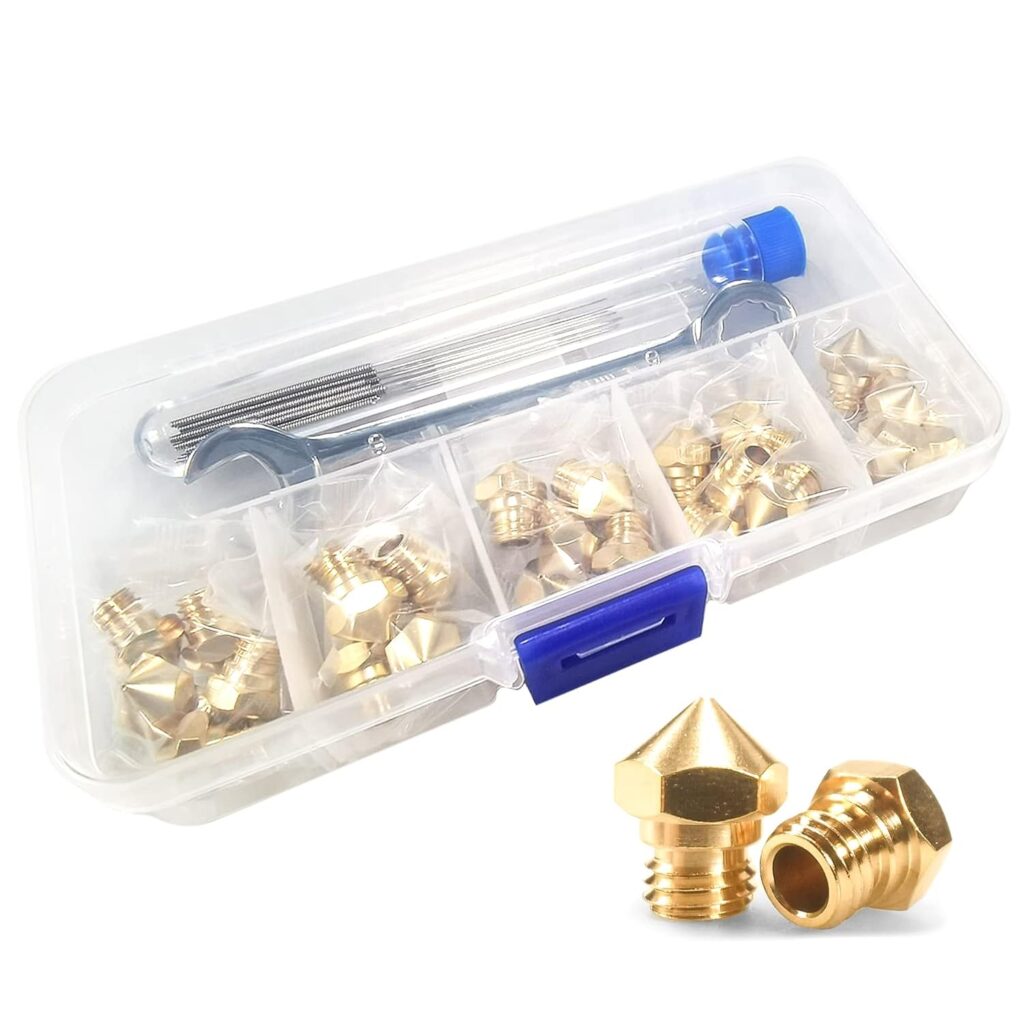

Warping
Warping is a prevalent issue in 3D printing that can impede the perfection of prints. It occurs when the print’s base cools unevenly, causing the edges to curl upward, thus detaching from the build platform. Identifying warping is straightforward; look for curled edges or a distorted base. The primary underlying cause is uneven cooling of the print material.
To mitigate warping, use a heated build platform to ensure consistent temperature. Additionally, applying an adhesive like glue stick or painter’s tape on the build plate can improve bed adhesion. Ensuring the print environment is draft-free can also aid in preventing uneven cooling.
Stringing
Stringing, often referred to as oozing, occurs when the filament leaks out of the nozzle while the extruder moves to a new location, resulting in thin strings of plastic between parts. Symptoms include fine threads or webs that disrupt the clean lines of a 3D model.
Combat stringing by calibrating retraction settings, which involve adjusting the speed and distance the filament retracts during non-print travel moves. Additionally, lowering the print temperature can help since higher temperatures increase the filament’s tendency to ooze.
Overheating
Overheating manifests as droopy or saggy prints, especially in overhangs and small parts. Identified by a rough or melted appearance on the surface of the print, overheating is often a result of excessively high printing temperatures or insufficient cooling.
To resolve overheating, optimize fan settings to ensure adequate cooling. Reducing the print temperature and printing at a slower speed can also help manage heat more effectively. Ensuring proper airflow around the print is critical for temperature regulation.

Ghosting/Ringing
Ghosting, or ringing, appears as ripples or waves adjacent to the edges of a model, usually following a sudden change in the printer’s direction. This issue is typically linked to vibrations and mechanical oscillations within the 3D printer.
Troubleshooting ghosting involves reducing print speed to minimize vibrations and checking that all belts and pulleys are properly tensioned and lubricated. Additionally, placing the printer on a stable surface can further reduce extraneous movement that contributes to ghosting.
Under-Extrusion
Under-extrusion is when the printer fails to extrude sufficient filament, resulting in thin, weak layers or even gaps in the print. Symptoms include incomplete layers, gaps in the walls, or parts that can be easily broken.
Tackling under-extrusion necessitates examining the filament path for obstructions, ensuring the nozzle is not clogged, and confirming that the extruder gears function properly. Verifying correct filament diameter settings in the slicer and increasing print temperature can also improve filament flow during extrusion.

Preventative Measures and Maintenance Tips
Prevention is a fundamental key to ensuring a smooth and efficient 3D printing process. By adhering to a series of preventative measures, users can notably reduce the frequency of common 3D printing problems, thereby enhancing their overall 3D printing experience. Below are a few best practices and maintenance tips that can help in achieving consistent and high-quality prints.
First and foremost, maintaining a clean 3D printer is crucial. Dust, debris, and remnants from previous prints can accumulate on various components of the printer, like the build plate and extruder. Routine cleaning prevents these particles from interfering with the printing process. For optimal results, it is recommended to wipe the build plate with isopropyl alcohol and to regularly inspect the extruder for any build-up that might cause clogs.

Proper calibration of your 3D printer is another critical factor in preventing issues. Calibration ensures that the printer’s axes are aligned correctly, and the build plate is level, facilitating precise layer deposition. Conducting a regular calibration check helps to mitigate problems such as layer shifting or uneven prints. Most modern 3D printers come equipped with auto-leveling features, but manual checks are still advisable to catch any discrepancies.
Using high-quality materials is also essential in preventing 3D printing issues. Low-quality filaments can be contaminated or possess inconsistent diameters, leading to extruder clogs or poor print quality. Investing in reputable filament brands can contribute significantly to the reliability and success of your prints. Additionally, storing filament properly in a dry, cool environment prevents moisture absorption, which can affect print integrity.
LINK to: 5 Best Entry-Level 3D Printers for Home Businesses in 2024
Last but not the least, paying attention to firmware updates is necessary for maintaining the efficiency of your 3D printer. Firmware updates frequently contain important bug fixes and enhancements that can resolve underlying issues and improve the printer’s overall performance.
By incorporating these practices—keeping the machine clean, ensuring proper calibration, using high-quality materials, and staying current with firmware updates—users can substantially minimize the risk of encountering common 3D printing problems, leading to more consistent and successful prints.